소개: PyTorch의 nn.Linear, 명확하게 설명하다
Updated on
nn.Linear는 PyTorch에서 가장 기본이 되는 블록 중 하나입니다.
간단한 Multi-Layer Perceptron(MLP), Transformer, 대규모 딥러닝 시스템까지 무엇을 만들든, 선형 계층은 데이터에 빠른 affine 변환을 수행하는 핵심 요소로 거의 모든 곳에 사용됩니다.
PyTorch 2.x에서는 linear layer가 업데이트된 커널, 컴파일러 최적화(torch.compile), 더 나은 GPU 가속의 이점을 누립니다. 이 업데이트된 가이드는 기초부터 현대 딥러닝에서의 활용까지, 알아야 할 모든 내용을 다룹니다.
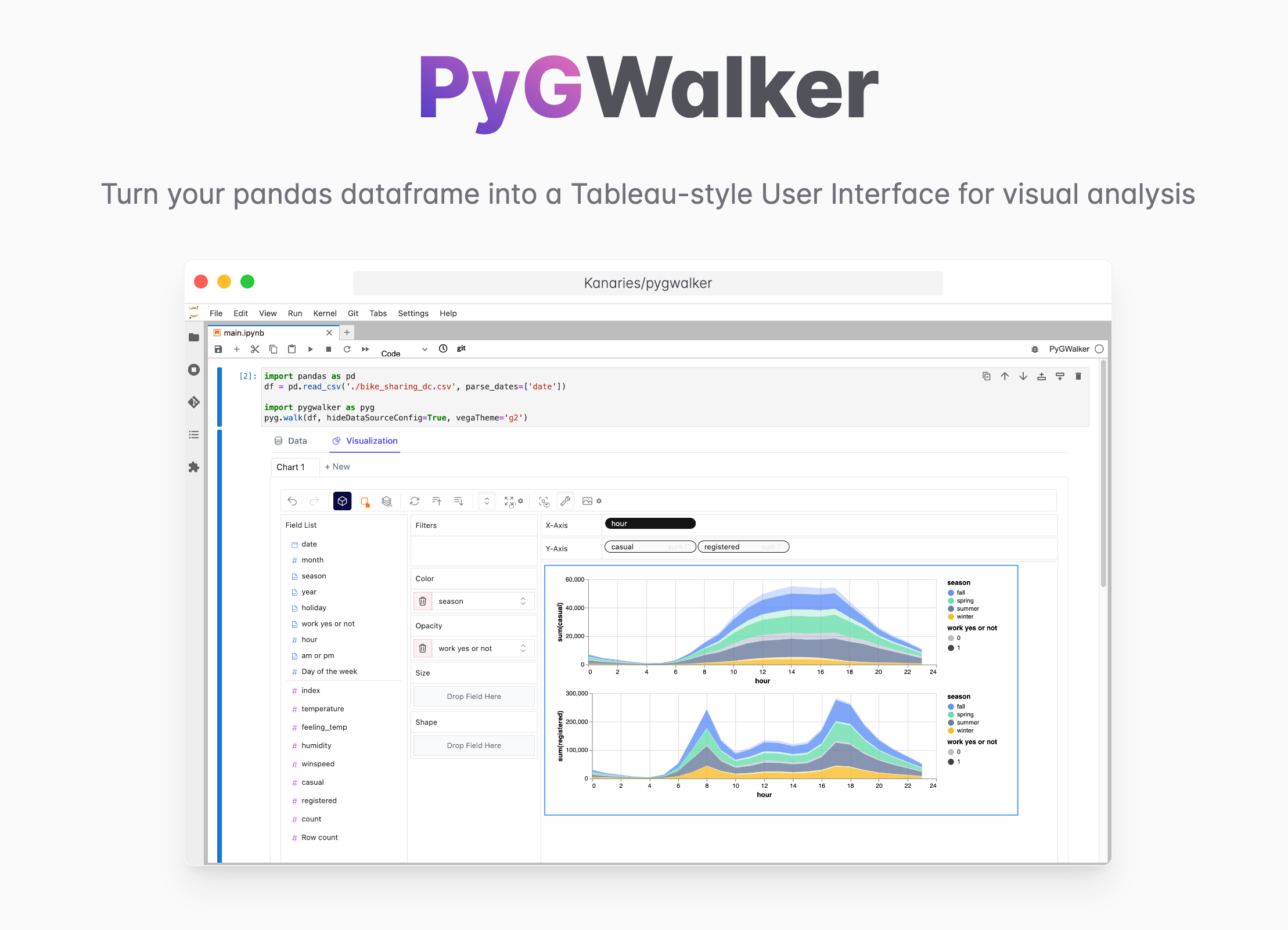
Python Pandas DataFrame으로부터 노코드로 빠르게 데이터 시각화를 만들고 싶나요?
PyGWalker는 시각화를 활용한 탐색적 데이터 분석(EDA)을 위한 Python 라이브러리입니다.
pandas 또는 polars DataFrame을 Jupyter Notebook 안에서 Tableau와 비슷한 UI로 바꿔 줍니다.
Understanding nn.Linear in PyTorch
What is nn.Linear?
nn.Linear는 입력 데이터에 affine 변환을 적용합니다:
[ y = xA^T + b ]
x: 입력 텐서A: 가중치 행렬 (out_features × in_features)b: bias 벡터 (out_features)y: 출력 텐서
이 모듈은 두 개의 필수 인자를 받습니다:
nn.Linear(in_features, out_features, bias=True)예시:
import torch
from torch import nn
linear_layer = nn.Linear(in_features=3, out_features=1)이렇게 생성됩니다:
- weight shape:
1 × 3 - bias shape:
1
How Does nn.Linear Work?
forward pass에서는 다음을 수행합니다:
- weight와의 행렬 곱셈
- bias 덧셈(활성화된 경우)
output = linear_layer(torch.tensor([1., 2., 3.]))
print(output)📌 Modern Usage: Batched Inputs
PyTorch의 nn.Linear는 마지막 차원에 대해 연산을 적용합니다.
그래서 다음과 같은 배치 형태에서 별도 처리 없이 자연스럽게 동작합니다.
2D inputs (batch, features)
[batch, in_features]3D inputs (batch, seq_len, features)
Transformer에서 흔히 사용되는 형태:
[batch, seq_len, in_features] → [batch, seq_len, out_features]예시:
x = torch.randn(32, 128, 512) # batch=32, seq_len=128, hidden=512
linear = nn.Linear(512, 1024)
y = linear(x) # output: [32, 128, 1024]별도의 reshape가 필요 없습니다 — 이는 attention에서 Q, K, V projection을 구현할 때 특히 중요합니다.
Initializing Weights and Biases
PyTorch는 기본적으로 Kaiming Uniform 초기화를 사용하지만, torch.nn.init을 이용해 자유롭게 커스터마이즈할 수 있습니다.
import torch.nn.init as init
init.xavier_uniform_(linear_layer.weight)
init.zeros_(linear_layer.bias)When to use bias=False
다음과 같은 경우에는 bias를 끄는 일이 자주 있습니다:
- linear layer 뒤에 normalization layer가 바로 따라올 때
(예: Transformer의LayerNorm) - attention block의 Q/K/V projection layer
- residual block 내부의 linear layer
예시:
nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim, bias=False)Comparing nn.Linear and nn.Conv2d
| Layer | Best for | Operation | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
nn.Linear | 벡터, 펼친(flattened) 입력, MLP, Transformer | Affine transform | in_features, out_features |
nn.Conv2d | 이미지 데이터, 국소 공간 패턴 | Sliding window convolution | channels, kernel size, stride, padding |
핵심 차이점:
- Linear layer는 dense connection(모든 입력-출력 간 완전 연결)을 사용합니다.
- Conv2D는 공간적으로 국소적인 커널을 사용해 파라미터 수를 줄이고, 강한 inductive bias(공간 구조에 대한 사전 가정)를 제공합니다.
Applications of nn.Linear in Deep Learning
1. Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP)
layer = nn.Linear(256, 128)2. Transformer Models
표준 Transformer에서 linear layer는 다음에 사용됩니다:
- Q, K, V projection
- MLP feed-forward network
- 출력 head
예시:
q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_model, bias=False)3. Classification Heads
classifier = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, num_classes)4. Autoencoders
Encoder와 decoder 모두에서 linear layer를 사용해 정보를 압축하고 복원합니다.
Using nn.Linear in a PyTorch Model
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch import nn
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(10, 5)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(5, 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
return self.fc2(x)
net = Net()Modern PyTorch 2.x Tips (Important!)
🚀 1. torch.compile로 linear layer 최적화
model = torch.compile(net)컴파일을 통해 연산을 fusion하여 GPU 성능을 높일 수 있습니다.
⚡ 2. GPU에서 더 빠른 학습을 위한 AMP
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast():
output = model(x)📉 3. 추론용 Quantized Linear
import torch.ao.quantization as quant모델 크기를 줄이고 추론 속도를 높이는 데 유용합니다.
🔧 4. 커스텀 fused 연산에는 F.linear 사용
import torch.nn.functional as F
y = F.linear(x, weight, bias)여러 연산을 수동으로 결합해 커스텀 연산을 만들 때 유용합니다.
Common Errors and How to Fix Them
1. Shape Mismatch
RuntimeError: mat1 and mat2 shapes cannot be multiplied해결: 입력의 마지막 차원이 in_features와 일치하는지 확인합니다.
2. 3D 입력을 nn.Linear가 처리하도록 두지 않고 reshape하는 경우
불필요한 reshape는 피하세요 — nn.Linear는 이미 3D 입력을 지원합니다.
3. 정수 텐서를 섞어 쓰면서 .float()를 잊는 경우
x = x.float()Conclusion
nn.Linear는 겉보기에는 단순하지만, PyTorch에서 매우 기본적이고 중요한 모듈입니다.
MLP에서 Transformer, 최신 생성 모델에 이르기까지, 오늘날의 딥러닝 시스템에서 대부분의 연산량은 linear layer에서 발생한다고 해도 과언이 아닙니다.
다음 내용을 이해하면:
- 동작 원리
- 다양한 입력 shape 처리 방식
- PyTorch 2.x에서의 최적화 방법
신경망 모델을 설계하고 디버깅하는 데 훨씬 더 효율적으로 대응할 수 있습니다.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a bias vector in nn.Linear?
bias는 입력과 무관하게 출력 값을 평행 이동시킬 수 있게 해 줍니다.
특히 입력 데이터가 0을 중심으로 분포하지 않을 때, 모델의 표현력을 높이는 데 도움이 됩니다.
How do you initialize weights and biases?
PyTorch가 자동으로 초기화를 수행하지만, 필요하다면 torch.nn.init(예: Xavier initialization)을 사용해 원하는 방식으로 재초기화할 수 있습니다.
Difference between nn.Linear and nn.Conv2d?
nn.Linear는 dense한 affine 변환을 적용하며, MLP나 Transformer에 주로 사용됩니다.
nn.Conv2d는 공간적인 convolution을 적용하며, 이미지 데이터를 다루는 CNN에서 주로 사용됩니다.